
Foundation of a Manufactured Home, Manufactured Home Foundation Types And Requirements Guide
Introduction
A strong foundation is one of the most important components of any home. It helps you forget about problems related to the durability of your home. Before starting your manufactured home construction process, make sure that you have a strong foundation to put your house on. In fact, it should be your highest priority.
If you don’t know which type to choose, continue reading this article to find out the manufactured home foundation requirements and discover the type that will best fit your home.
Requirements for Manufactured Home Foundation Inspections
When you buy a new manufactured home, make sure that you discuss all the requirements with the manufactured home dealer. If the home is already used, you can always tell the seller to remedy the problems before buying it. If they refuse to do so, it is up to you if you are willing to pay for the repair or have a look at other properties.
Keep in mind that FHA-manufactured home foundations have to meet certain requirements. Here are a few basic FHA manufactured home requirements for you to consider:
-
Mortar joints in the piers
-
Wheels, tongue, and axles removed
-
8” thick (2’ x 2’) concrete footing
-
Stabilizer structures that keep the home from moving in the longitudinal and transverse directions
-
Earth anchors and straps to resist hurricane wind loads
-
6 mil vapor barrier on the ground within the crawl space
Besides the basic requirements mentioned above, let’s find out more detailed standards of manufactured Home Foundation Inspections:
1. Excavation
Excavation for foundation footing or walls should reach below the soil subjected to characteristic volume or seasonal change to unaffected soil that provides sufficient bearing. If the areas are more prone to frost, the footing should be positioned below the frost depth below grade. If the soils are expansive in those areas, you will need to carry out seasonal wetting and drying.
2. Foundation Material
Solid materials like concrete and ABS foundation pads can be used to construct the foundation and footing.
3. Structural Requirements
First of all, you'll need to have an acceptable foundation system that can support exterior walls, piers, columns, and marriage wall posts. They can vary depending on the character of the soil. The height of the floor should also be 18 inches from the finished grade to the foundation at all points. Pier foundation footings are crafted with ABS pads or pre-cast concrete. Typical piers are concrete masonry units with 16" x 16" x 8".
Regarding the ground level, it should be 18 inches below the bottom of the floor joists and 12 inches below the bottom of the chassis beam. If you also need to repair the equipment present there, you can access the area under the floor, having the ground level below the floor joists 2 feet or more.
4. Foundation Design
Here you must meet all the requirements related to all gravity, lateral, and occupancy loads. Let's consider the lateral loads, such as seismic or wind activities. In this case, the vertical anchorage is of utmost importance. Your manufactured home should be attached to the foundation securely.
Manufactured Home Foundation Types
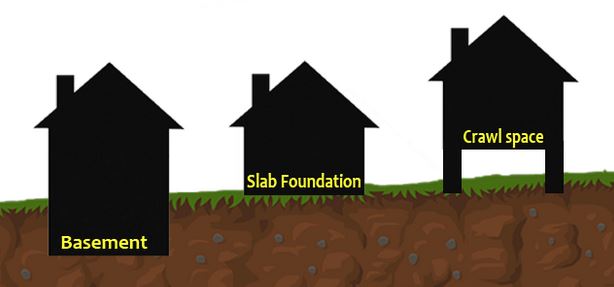
There are different types of foundations for manufactured homes. Each of them has its own unique structure, advantages, and disadvantages.
Some of the main manufactured home foundation types include:
-
Pier and beam foundation
-
Slab foundation
-
Crawl space foundation
-
Basement foundation
Pier and beam foundation
This type of foundation is the most popular one for manufactured homes. With this foundation system, anchors are placed into the ground to hold the home and protect it from wind forces. After placing the anchors into the ground, steel straps are attached to connect the piers with the steel frame of the manufactured home.
You shouldn’t worry about the effectiveness of this system as it has been used for ages. There are already many types of tricks that constructors use to make sure your home is stable. This kind of protection provides excellent protection against winds, floods, frost, and moving soil.
|
Pier and beam foundation |
|
|---|---|
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
Easy and cheap to install |
The piers may move separately, and your home can become unlevel |
|
Offers flood and frost resistance |
Harder to store items |
|
Takes less time compared to other systems Can be used in seismic areas |
Having a dirt or stone floor under the home makes it hard to do repairs |
|
Wind zone resistance – Effective wind zone resistance |
|
|
Can be used in seismic areas |
|
Slab foundation
Slab foundation is more like a platform for support when it comes to manufactured homes. The slab is placed on the ground with anchors embedded in the concrete. In places, where the ground is prone to freeze during winters, a slab foundation is poured over piers to add more stability. A slab foundation without piers is called floating a floating slab.
|
Slab foundation |
|
|---|---|
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
One of the most affordable systems |
Not suitable for sloping lots |
|
The time needed for this foundation is minimal |
The slab can move. This may damage plumbing running through it |
|
Can be used in seismic areas |
Be aware of the frost line in your areas and insulate it if needed |
|
Can be used in flood-hazard areas |
|
|
A crawl space between the slab and home |
|
Crawl space foundation
A crawl space foundation is designed with an excavated floor and is usually built using poured concrete footers put inside the soil. As you can guess from the name, the crawl space foundation creates a deep crawl space within the foundation of the home. They are perfect for areas with high humidity. However, manufactured homes are not attached to crawl spaces.
|
Crawl space foundation |
|
|---|---|
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
Middle price range compared to other systems |
Not ideal for hurricane-prone areas |
|
Completed by the time the home arrives to the site |
Not intended for flood-prone areas |
|
Effective in areas with higher winds |
|
|
Good earthquake resistance |
|
|
Can be used in almost any climate |
|
Basement foundation
Basement foundations are good for adding extra living space to your house. This type is considered to be the most specific as they need to carry out precise measurements to match your house. Besides that, basement foundations have building codes that differ from city to city. So, you should meet all the requirements depending on the place you live.
|
Basement foundation |
|
|---|---|
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
Good earthquake resistance |
The most expensive option due to their construction time and materials |
|
Real estate classification and finance approval |
Takes longer to build and install due to their complicated structural design |
|
Can be used in areas of frost |
Cannot be used in flood hazard areas as there is always a chance your basement will get flooded |
|
Provides extra living space |
|
|
Resists wind loads, even giving you a place to take cover in high winds |
|
FHA Manufactured Home Requirements
If you are thinking about an FHA loan, your home should also meet the following FHA manufactured home requirements:
-
Your manufactured home should be built after June 15, 1976
-
The living area should be at least 400 square feet
-
It should be a single-family dwelling
-
If your manufactured home is new, you should have a one-year warranty from its manufacturer
-
The home site needs to have access to water and sewer facilities
-
It should comply with the manufactured home installation requirements issued by the HUD
-
The home is permanently attached to land according to local building guidelines
-
The home should be taxed as real estate
Manufactured home foundation certification
Your lender will require a manufactured home foundation certification from you to verify that the foundation is present, permanent, and its functional. A permanent foundation is one that's constructed of durable materials like concrete, treated wood, or mortared masonry.
You should keep in mind that according to HUD the manufactured home foundations must “have attachment points to anchor and stabilize the manufactured home to transfer all loads to underlying soil or rock. The design must comply with FHA guidelines. For existing homes, a Structural Engineer is required to certify that the foundation meets the FHA requirements. The HUD Permanent Foundations Guide for Manufactured Housing, publication number HUD-007487 is the basis for the FHA requirements. The permanent foundations shall be structurally developed in accordance with this document or be structurally designed by a licensed professional engineer.”
Cost of permanent foundation for a manufactured home
As you can see, there are many benefits to having a permanent foundation for your manufactured home. One of them is that your manufactured home will become real estate. But how much would it cost to get a permanent foundation?
On average, constructing a manufactured home foundation costs between $3500 and $200.000. However, most manufactured homeowners pay between $4500 and $12.000 based on their requirements and the foundation type.
Why You Need a Manufactured Home Foundation Inspection
There are several reasons you should consider a manufactured home foundation inspection in your state. One of the most important reasons is that before purchasing a manufactured home, a licensed professional is required to inspect it. Your lender or bank will request a written report confirming that the manufactured home foundation meets the HUD standards.
Besides that, once the new manufactured home is constructed in the factory, it will later be installed at the place you want. This time again, your lender will request certification from a licensed inspection contractor to make sure that the foundation complies with the set rules.
How a Manufactured Home Foundation Inspection Works

Please note that manufactured homes are different from regular homes. The foundation of manufactured homes is mostly constructed on piers, while the home is attached to the l-beams. That’s the main reason your foundation should be inspected.
Here are a few things you should consider when searching for a manufactured home foundation inspector:
-
Do they have a license?
-
Do they inspect whether the home is securely attached to the foundation or not?
-
Can they give you the Engineering Certification?
If the answer to these questions is a “yes”, then they can be a good fit for you!
Manufactured Homes Regulation in Different States
California
According to California manufactured housing regulations, you can choose among different types of foundations. Frost-protected shallow foundations are increasingly common and are approved by the IRC. These foundations offer a significant advantage to manufactured home installations because they obviate the need to dig to the frost line while avoiding the problems that might arise with floating slabs.
Oregon
According to the Oregano manufactured housing regulations, acceptable types of foundations should incorporate the foundation footing, pier, and shimming requirements into one device.
Foundation materials made from wood or wood by-products exposed to excess moisture, such as under open porches and decks, shall be cedar, redwood, pressure-treated lumber, or wood-polymer composite. Besides that, Piers shall be capable of transmitting the vertical live and dead loads to the foundation below. Every pier shall be supported by a footing.
Washington
Here are the minimum foundation structural requirements based on Washington manufactured housing regulations:
-
The concrete pad, or footing, must be placed on firm and level ground.
-
The support piers must be 8” x 8” x 16” concrete blocks and placed as follows: There must be at least 12 inches of clearance from the bottom of the steel beam to the ground. If the support piers are 3 feet high or less, you can use a single stack.
-
The gap between the pier cap and the steel beam can be filled with wood that is not more than 2x material.
-
The wood shims used to level the home must be 4 to 6 inches long and a maximum of 1½ inches thick.
New Mexico
Just like is the case with most states, New Mexico manufactured housing regulations include the existence of the following items for the purchasing of a manufactured home in this state:
-
Permits
-
Site work
-
Non-permanent foundations
-
Permanent foundations
-
Water supply and testing
-
Anchoring
-
Retaining walls
-
Installation of fireplaces and wood-burning stoves
-
Drainage systems
-
Electrical supply and systems
-
Connection to LP and Natural gas
Arizona
According to Arizona manufactured housing regulations, each manufactured home shall have provisions for support/anchoring or foundation systems that will resist overturning and lateral movement (sliding) of the manufactured home as imposed by the respective design loads.
The manufacturer of each home is required to make provision for the support and anchoring systems but is not required to provide the anchoring equipment or stabilizing devices. The anchoring equipment should be certified by a registered professional engineer or architect to resist these specified forces in accordance with testing procedures.
Not sure which foundation type to choose for your manufactured home? At Homes Direct, we will help you discover the best option based on the specific features of the area you’re going to locate your manufactured home. Contact us, and let’s discuss the details together!


